Cognitive Hierarchy Test
Understanding the complexities of human cognition is vital for advancing both psychological research and its practical applications. The Cognitive Hierarchy Test is designed to assess and analyze your different levels of cognitive processing, from basic memory and attention to higher-order thinking skills. This test provides valuable insights into how individuals perceive, interpret, and respond to various cognitive processes. By measuring a range of cognitive functions, the Cognitive Hierarchy Test helps identify patterns and hierarchies in mental processing.
To take the test, enter your input below.
Question 1 of 75
I often forget what I was just thinking about.
| Disagree | Agree |
NEXT
The IDRLabs Cognitive Hierarchy Test is developed by IDRLabs. The IDRLabs Cognitive Hierarchy Test is inspired by research in cognitive processes and neuroscience and measures different layers of cognitive functioning.
The test provides feedback such as the following:
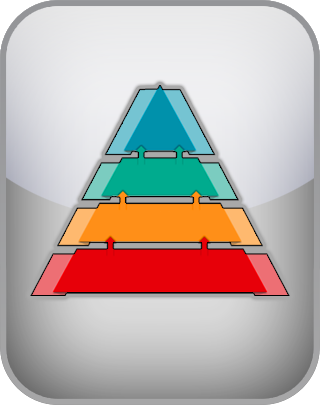
The cognitive hierarchy is a conceptual model that organizes various cognitive functions and processes into different levels of complexity and integration. Each level depends on the solid foundation of the levels below it, meaning that effective functioning at higher levels (like critical thinking and metacognition) relies on well-developed abilities at lower levels (like sensory, perception, and attention).
At the lowest levels of the hierarchy are sensory perceptions—seeing, hearing, touching, tasting, and smelling—through which individuals receive and initially process information from the environment. This sensory data is then filtered and focused on through attention processes, which determine what information is prioritized and further processed.
As information moves up the hierarchy, it enters the realms of memory, where it is stored and retrieved, and learning, where it is assimilated into knowledge and skills. Higher skill are the levels of reasoning and decision-making, where this information is used in logical thinking, problem-solving, and making choices.
At the apex of the hierarchy is critical thinking and metacognition, where individuals not only process and use information but also reflect upon, understand, and regulate their own cognitive processes. This highest level involves sophisticated mental abilities (e.g., mentalizing) that enable individuals to analyze their thinking, make informed decisions, and learn from their experiences.
Human cognitive processes encompass the intricate mental activities that enable individuals to acquire knowledge, understand, and interact with their environment. These processes involve various functions such as perception, attention, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making.
Perception is the initial cognitive process that allows humans to interpret and organize sensory information from the environment. It involves recognizing and making sense of stimuli through sight, sound, touch, taste, and smell. This foundational process is crucial for effective interaction with the world.
Attention, the ability to focus on specific stimuli while ignoring others, plays a vital role in cognition. It allows individuals to prioritize information, manage distractions, and sustain concentration on tasks. Selective attention, in particular, enables one to filter out irrelevant information, enhancing cognitive efficiency.
Memory, another critical cognitive process, involves encoding, storing, and retrieving information. It is divided into different types: sensory memory (brief retention of sensory information), short-term memory (holding information temporarily for analysis), and long-term memory (storing information over extended periods). Memory is essential for learning, as it enables the retention and application of knowledge.
Language, a unique human capability, involves the comprehension and production of spoken, written, and signed communication. It is a fundamental tool for expressing thoughts, sharing information, and understanding others. Language development and usage are deeply intertwined with other cognitive processes, such as memory and attention.
Problem-solving and decision-making are higher-order cognitive functions that involve evaluating information, generating solutions, and making choices. These processes require critical thinking, reasoning, and the ability to anticipate outcomes. Effective problem-solving often involves creativity and flexibility, allowing individuals to navigate complex and novel situations.
In summary, human cognitive processes are essential for interpreting the world, acquiring and utilizing knowledge, and making informed decisions. These processes are interconnected, collectively contributing to the richness of human thought and behavior. Understanding these cognitive mechanisms is crucial for fields ranging from psychology and education to artificial intelligence and human-computer interaction.
The IDRLabs Cognitive Hierarchy Test is inspired by psychometric methodology and research in cognitive processing and hierarchical structure. While the IDRLabs Cognitive Hierarchy Test is inspired by scientific research, it cannot be used to provide clinical assessments or an accurate evaluation of your features. Clinical assessments should always be done in cooperation with a mental health professional. For more information about any of our online tests and quizzes, please consult our Terms of Service.
References
- Eysenck, M.W., & Keane, M.T. (2015). Cognitive Psychology: A Student's Handbook (7th ed.). New York: Psychology Press.
- Dunlosky, J., & Bjork, R.A. (Eds.). (2008). Metacognition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications.